How It Works: End-to-End Data Flow
This document describes the complete workflow of how data flows through the system, from initial JSON input to final storage in the databases.
1. Data Entry Point (Ingestion API)
The system receives data through a REST API built with Ballerina. The API accepts JSON payloads for entity creation and updates.
Example JSON Input
{
"id": "entity123",
"kind": {
"major": "Person",
"minor": "Employee"
},
"name": {
"startTime": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"endTime": "",
"value": "John Doe"
},
"metadata": {
"department": "Engineering",
"role": "Software Engineer"
},
"attributes": {
"expenses": {
"columns": ["type", "amount", "date", "category"],
"rows": [
["Travel", 500, "2024-01-15", "Business"],
["Meals", 120, "2024-01-16", "Entertainment"],
["Equipment", 300, "2024-01-17", "Office"]
]
}
},
"relationships": {
"reports_to": {
"relatedEntityId": "manager123",
"startTime": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"endTime": "",
"id": "rel123",
"name": "reports_to"
}
}
}
2. Data Transformation (Ingestion API → Core API)
2.1 JSON to Protobuf Conversion
The Ingestion API converts the JSON payload into a protobuf Entity message. This conversion happens in the convertJsonToEntity function:
Conversion Process Flowchart
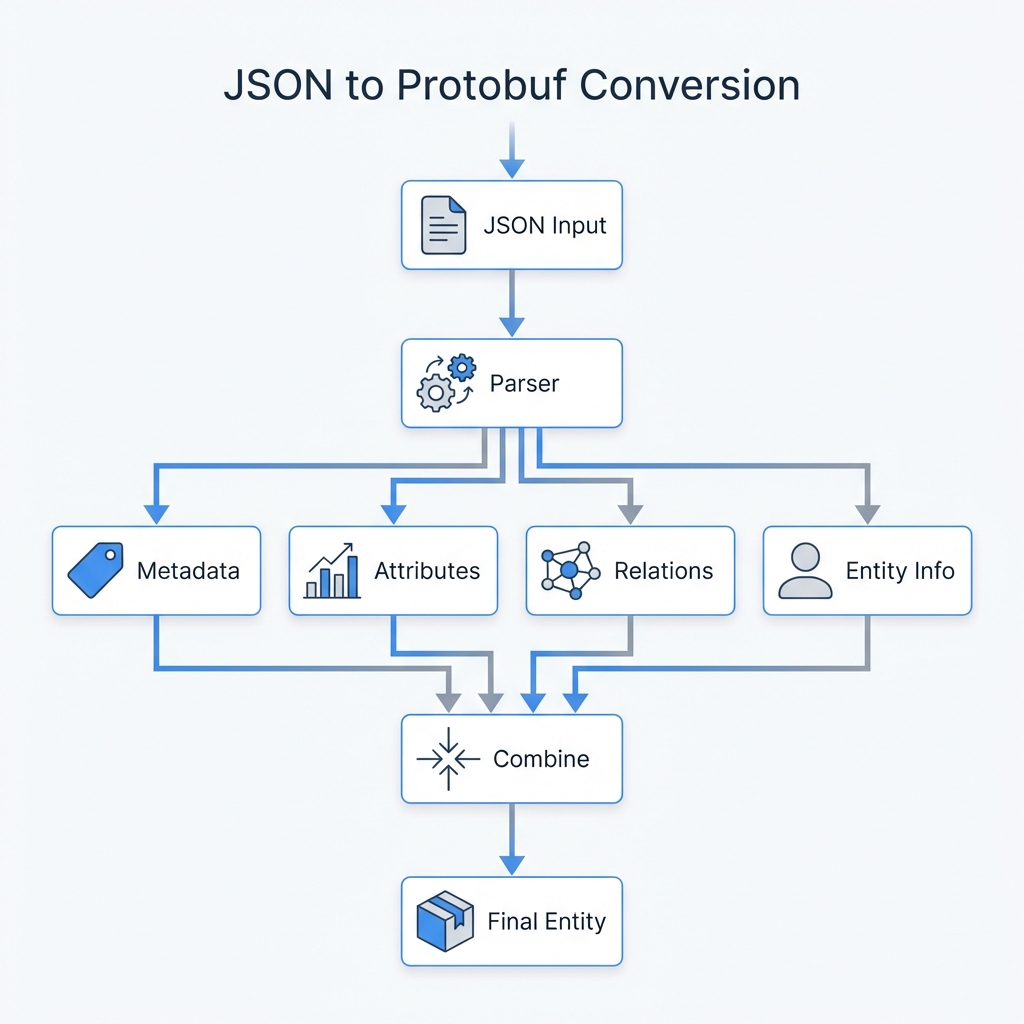
Conversion Details
The conversion process involves several key transformations:
- Metadata Processing: Each metadata key-value pair is converted to a protobuf
Anytype usingpbAny:pack() - Attributes Processing: Each attribute is converted to a
TimeBasedValueListcontaining time-based values withstartTime,endTime, and packed values - Relationships Processing: Each relationship is converted to a
Relationshipobject with all required fields - Entity Assembly: All processed components are combined into the final
Entityprotobuf message
The flowchart above shows the complete data transformation pipeline from JSON input to protobuf output.
2.2 gRPC Communication
The converted protobuf message is sent to the CORE service via gRPC. The communication happens on port 50051.
3. Core API
The Core API receives the protobuf message and processes it through multiple steps:
3.1 Create Entity Flow
The Core API processes entity creation through a systematic three-step approach:
Step 1: Metadata Storage (MongoDB)
- The system first saves the entity's metadata to MongoDB
- This includes all key-value pairs from the
metadatafield in the JSON payload - MongoDB's flexible document structure allows for schema-less storage of metadata
- The entity ID serves as the document identifier for quick retrieval
Step 2: Entity Creation (Neo4j)
- The core entity information is stored in Neo4j as a graph node
- This includes the entity ID, kind (major/minor), name, and timestamps
- Neo4j's graph structure enables efficient relationship traversal and queries
- The entity becomes a node in the graph database with the
Entitylabel
Step 3: Relationship Management (Neo4j)
- All relationships defined in the JSON payload are created in Neo4j
- Each relationship becomes a directed edge between entity nodes
- Relationship properties include start/end times and relationship metadata
- This enables complex graph queries and relationship traversal
3.2 Data Storage
MongoDB Storage (Metadata)
The metadata is stored in MongoDB as a document:
{
"_id": "entity123",
"metadata": {
"department": "Engineering",
"role": "Software Engineer"
}
}
Neo4j Storage (Entity and Relationships)
The entity and its relationships are stored in Neo4j using a graph-based approach:
Entity Node Creation
- Each entity becomes a node in the Neo4j graph with the
Entitylabel - The node contains core entity properties including:
- Unique entity identifier (
id) - Entity classification (
kind_majorandkind_minor) - Entity name and display information
- Temporal information (
createdandterminatedtimestamps)
- Unique entity identifier (
- This structure enables efficient entity lookup and management
Relationship Creation
- Relationships between entities are represented as directed edges in the graph
- Each relationship has a specific type (e.g.,
REPORTS_TO,MANAGES,WORKS_FOR) - Relationship properties include:
- Unique relationship identifier
- Temporal validity (
startTimeandendTime) - Additional relationship metadata
- The directed nature allows for complex relationship traversal and queries
Graph Query Capabilities
- The graph structure enables powerful relationship queries
- Users can traverse relationships in any direction
- Complex multi-hop queries are efficiently supported
- Temporal queries can find relationships active at specific time periods
4. Data Retrieval Flow (Read API)
4.1 Read Entity Flow
The Core API retrieves entity data through a systematic three-step aggregation process:
Step 1: Metadata Retrieval (MongoDB)
- The system first queries MongoDB to retrieve the entity's metadata
- This includes all key-value pairs associated with the entity ID
- MongoDB's document-based storage enables fast metadata lookup
- The metadata provides additional context and properties for the entity
Step 2: Entity Information Retrieval (Neo4j)
- Core entity information is fetched from Neo4j using the entity ID
- This includes fundamental entity properties such as:
- Entity classification (kind major and minor)
- Entity name and display information
- Creation and termination timestamps
- Neo4j's graph structure enables efficient entity node lookup
Step 3: Attribute Retrieval (PostgreSQL)
- Entity attributes are retrieved from PostgreSQL using the entity ID
- This includes all time-based attribute values stored in dynamic tables
- Attribute data includes:
- Attribute names and their corresponding values
- Temporal information (start and end times for each value)
- Data type information for proper value interpretation
- PostgreSQL's relational structure enables efficient attribute querying and time-based filtering
Step 4: Relationship Retrieval (Neo4j)
- All relationships connected to the entity are retrieved from Neo4j
- This includes both incoming and outgoing relationships
- Relationship data includes:
- Related entity identifiers
- Relationship types and properties
- Temporal validity information
- The graph structure enables efficient relationship traversal
Data Aggregation and Response
- All retrieved data is combined into a single entity response
- The system creates a comprehensive entity object containing:
- Core entity information from Neo4j
- Metadata from MongoDB
- All time-based attributes from PostgreSQL
- All associated relationships from Neo4j
- The aggregated data is returned as a complete entity representation with full temporal support
4.2 Data Transformation (Core API → Ingestion API)
The retrieved data is converted back to JSON in the Ingestion API before being sent to the client.